Analysis of Common Base Amplifier (CB) using h-parameter:
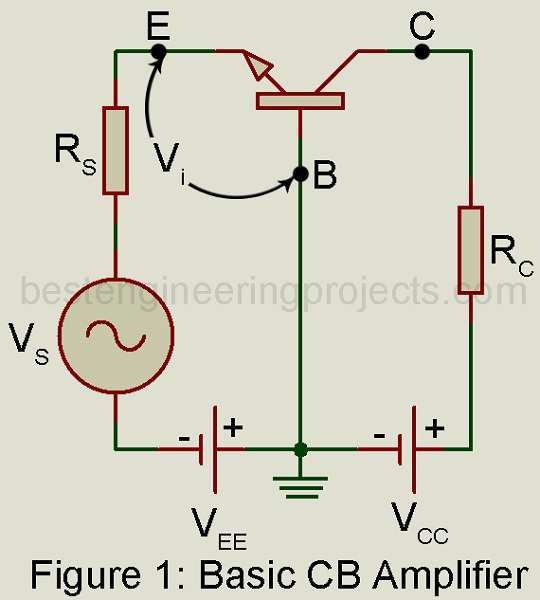
Figure 1 gives the basic circuit of a transistor (NPN type) used as a common base (CB) amplifier. In this case, Vs is the signal voltage, Vi is the actual voltage at the input terminals and V0 is the output voltage.
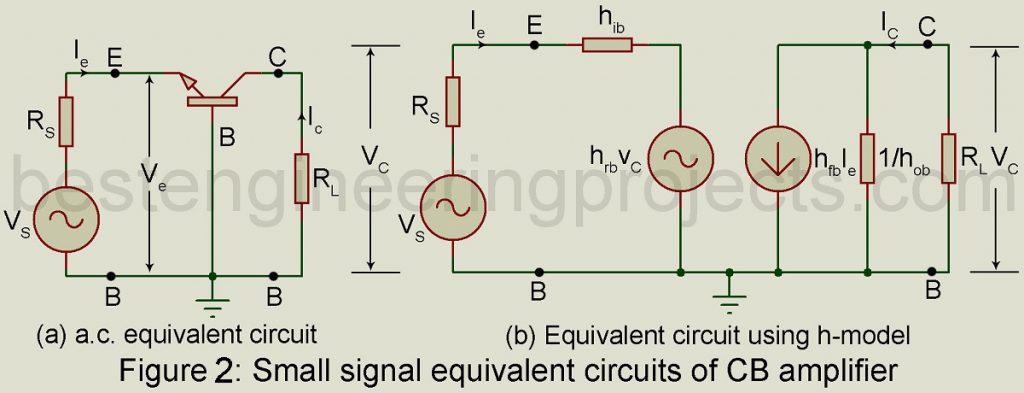
Figure 2(a) gives the a.c. equivalent circuit obtained on having removed the dc source. On replacing the CB transistor with its small-signal two generator h-parameter model we get the equivalent circuit of figure 1(b). Here also we assume sinusoidal input. Hence in the equivalent circuit of figure 2(b), we have used RMS valued of voltages and currents namely Ie, Ve, Ic, and Vc.
The equivalent circuit of figure 3 is similar to that of the CE amplifier as shown in the previous article Analysis of common emitter amplifier using h-parameter.
Hence analysis procedure is exactly the same. The expression of AI, Ri, AV, AIS, AVS and Yo are therefore, the same as for CE amplifier except that h-parameter for CB configuration are used. Thus we get::
Current gain …..(1)
Input resistance ……(2)
Where
Voltage Gain …..(3)
Output admittance …..(4)
Overall voltage gain …..(5)
Overall current gain …..(6)
Power Gain ……(7)
Equations (1) and (7) may be used to calculate current gain etc. in terms of CB h-parameter by corresponding CE h-parameters.
Example 1: A transistor in CB configuration is driven by a voltage source Vs of internal resistance Rs = 1000. The load impedance is a resistor RL = 4k. the h-parameters are : hib = 220, hrb = , hfb = – 0.98 and h0b =
. For this amplifier, calculate the current gain AI, input resistance Ri, voltage gain AV, overall voltage gain AVS, overall current gain AIS output resistance R0 and power gain Ap.
Solution:
Current gain
Input impedance
Voltage gain
Overall voltage gain
Overall current gain
Output admittance
Hence M
Power gain